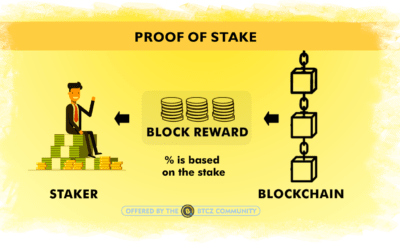
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake (PoS) model states that a person can validate block transactions according to how many coins they hold. This means that the ownership (stake) of more coins leads to the increase of the validating power and the associated rewards.
How Proof of Stake Works
Basic Concept
- Validators stake coins as collateral
- Validation power proportional to stake
- No mining hardware required
- Energy efficient
Validation Process
- Validators selected based on stake size
- Must maintain minimum stake
- Rewards distributed to validators
- Penalties for malicious behavior
Advantages of PoS
Energy Efficiency
- No power-intensive mining
- Environmentally friendly
- Lower operating costs
- Reduced carbon footprint
Economic Security
- Validators risk their stake
- Expensive to attack network
- Financial incentive for honesty
- Reduced hardware requirements
Potential Concerns
Centralization Risks
- Rich get richer effect
- High entry barriers
- Concentrated power
- Wealth-based control
Security Considerations
- Nothing at stake problem
- Long-range attacks
- Initial distribution issues
- Less proven than PoW
Comparison with PoW
Resource Usage
- PoS: Minimal energy use
- PoW: High energy consumption
Security Model
- PoS: Economic security
- PoW: Computational security
Entry Barriers
- PoS: Requires capital investment
- PoW: Requires hardware investment
BitcoinZ’s Position
BitcoinZ maintains PoW because:
- Proven security model
- Fair distribution mechanism
- True decentralization
- No initial coin ownership required